The blue side reflects blue light. Light travels into the eye to the retina, located on the back of the eye.

Color Physics The Science Of Color Particularly The Science Of Light And Color Perception Color Is Defined As A Visual Color Healing Prism Color Psychology
Light receptors within the eye transmit messages to the brain, which produces the familiar sensations of color.

How do we see color physics. We see objects of different colors. The color of an object is not actually within the object itself. The message is passed to the optic nerve and then on to the brain.
We see objects of different colors because light reflects. The color of the objects that we see is largely due to the way those objects interact with light and ultimately reflect or transmit it to our eyes. The physics of color perception involves energy wavelengths, reflections and signals zapping back and forth in our brains.
When sunlight hits a beach ball, we see only the light that bounces off of it. We see colour because of the rods and cones in our eyes there are about 120 million rods. Rather, the color is in the light that shines upon it and is ultimately reflected or transmitted to our eyes.
So what is color in science terms? In the circle at top right, the green pixels vary. But the reflection and refraction of light on an object is just one part of the story.
Some are sensitive to red color , some to blue and some to green. The science of color is full of surprises and the first is that seeing color is something that happens in your brain. How do we see colors?
The way we see colors isn't very straightforward. These two parts work together to control the amount of light entering your eye. Where does color come from?
The retina is covered with millions of light receptive cells called rods and cones. In the bottom circle, the blue pixels vary, so we see, at left, blue+red=magenta and, at right, blue+green=cyan. When you see objects you just receives light reflected or refracted from those objects which is perceived by your eye as color.
In the centre, where all three circles overlap, we see red+green+blue=white. How do we see colour? As a result, you can see all of the colours contained in white light.
Color is completely a phenomena of your eye. This mix of colors and white light is what lets us see colored objects. The way in which most of us actually see colour, is through the sensors in the retina of our eyes called rods and cones.
How do we see color? Where they overlap, we see red+green= yellow. Let's look at what happens in our eyes and brains when we see colour.
How is it possible that we can see it? The rods are sensitive to low light and the cones, which require a greater intensity of light, are sensitive to colour. How do we see colors physics?
Watch think open review body Learn more about color in this article. Different parts of the ball reflect different colors.
Newton observed that color is not inherent in objects. A green object reflects green light. Light receptors within the eye transmit messages to the brain, producing the familiar sensation of colour.
Even stranger, brown as a color is produced with red and green, but when you mix red and green light, it makes yellow. Now this is where it gets very interesting: In physics, color is associated specifically with electromagnetic radiation of a certain range of wavelengths visible to the human eye.
A blue object reflects blue light but absorbs all other waves. When a we see a banana the yellow light reflecting from it reaches our eyes and that yellow light is perceived by the different cone cells and the information is sent to the brain to be processed which afterwards is interpreted as yellow. The cornea will help direct the light towards your pupil and iris.
The iris is the colored part of your eye and the pupil is. The yellow side reflects yellow light. Your eyes create the code for color, as we will find out.
There are forbidden colors, colors that cannot be perceived by the human eye though they are a mix of perceivable colors. They are caused because the cones devoted to complimentary colors will. Color, the aspect of any object that may be described in terms of hue, lightness, and saturation.
Eye contains three types cells (cones) red,blue, green, these are activated by different wavelengths of light in different way and generate different colors you see. Red, green, and blue are considered the primary colors because they are fundamental to human vision. However, since science got involved, we can emit certain wavelengths of light, or mixtures of these, and declare them to be red or cyan or hyacinth or blue.
The cornea is a clear thin layer on the outside of your eyes. The human eye is sensitive to a band of electromagnetic radiation that lies in the wavelength range between 400 and 700 nanometers, known as the visible light spectrum. The resulting signal is zapped along the optic nerve to the visual cortex of the brain, which processes the information and returns with a color:

Do Yellow Bug Light Bulbs Work 1000bulbscom Blog Visible Light Electromagnetic Spectrum Visible Light Spectrum

How We See Color Color Theory Colour Theorist Color

Color Theory Lessons - Color As Light Elementary Art Color Theory Color Theory Lessons

How Do We See The Red Color Fizik

Color Wavelength Science Education Physics And Mathematics Physics

Visible Light - Windows To The Universe Visible Light Physical Science Physics

Visible Light Spectrum Poster Visible Light Spectrum Visible Light Electromagnetic Spectrum

Ks3 Physics - Light Waves - Revision 6 Light Science Light Wave Science

Science Of Ascension Light Science Light Wave Electromagnetic Spectrum

Photography Color Theory The Science Of Primary Colors Rgb Color Vision Color Vision Deficiency Color Wavelengths

Light Color Strongly Affects Environmental Impact Electromagnetic Spectrum Full Spectrum Light Visible Light

Inner Outer Light Physics And Mathematics Visible Light Teaching Science

Molecular Expressions Microscopy Primer Physics Of Light And Color - Human Vision And Color Perception Visible Light Visible Light Spectrum Color Vision

Fileprism-rainbowsvg Prism Light Colors Physics
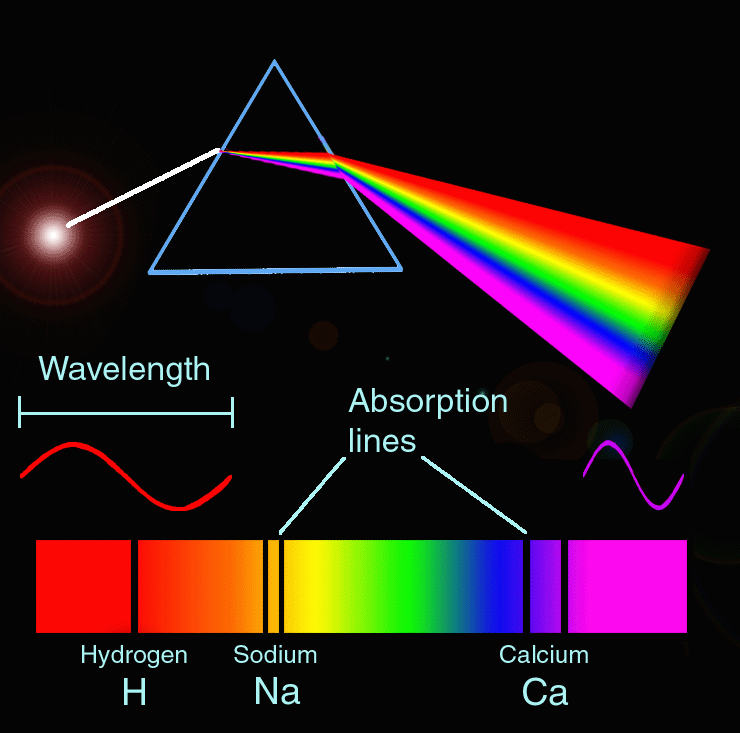
Spectroscopy The Diagram Shows What A Spectrum Is And How It May Contain Absorption Lines These Lines Can Be Ma Physics And Mathematics Physics Science Books

Importance Of Perception Of Colors And Light Properties Physics Physics And Mathematics Physics Teaching Ideas

What Is Visible Light Visible Light Visible Light Spectrum Science Fair Projects

Visible Light Diagram Color Electromagnetic Spectrum Light Wave Frequency Educational School Physics Vecto Visible Light Electromagnetic Spectrum Light Wave

Color Or Colour See Spelling Differences Is The Visual Perceptual Property Corresponding In Humans To The Categori Secondary Science Teaching Science Physics
How Do We See Color Physics. There are any How Do We See Color Physics in here.